ReadyChef uses both PHP and SQL to manage its data, so I have drawn up both a UML diagram and an ERD.
Database ERD
The ERD consists of nine tables with eight relationships.

account:
used to store data about the user account
id : INT PK
Used to identify a user even if they update their username
username : STRING
a unique string used to log in
hash : STRING
the user’s password hash, including salt and algorithm type
password_set : DATETIME
No current plans for this data field, but it can be used to warn the users that their password is getting old, or to force password changes for admins.
login_history:
used to track login attempts to prevent brute force attacks or DDoS
account_id : INT FK
Links the login attempt to a user account. It’s possible this would be better if it were linked to username instead.
success : BOOL
Indicates whether the login attempt was successful (correct password) or failed (incorrect password)
login_time : DATETIME
The time of the login attempt
ingredient:
used to store data about ingredients, and to normalize recipes
id : INT PK
A unique identifier for the ingredient. Saves disk space, instead of using VARCHAR as the key
name : STRING
The user readable name of the ingredient.
recipe:
id : INT PK
Unique identifier for the recipe
name : STRING
Not shown in the ERD (by mistake)
User readable name of the recipe
instructions : STRING
How to make the recipe, step by step.
category:
used for sorting recipes and ingredients in order to meet dietary restrictions (e.g. recipes using ingredients with dairy are left out if requested)
id : INT PK
Unique identifier for the category
name : STRING
Human readable name of the category (e.g. dairy, meat, etc)
user_has_ingredient:
used to create a M:N relationship between users and ingredients
account_id : INT FK
relation to account table
ingredient_id : INT FK
relation to ingredient table
date_purchased : DATE
Allows program to determine expected EOL for food item.
recipe_has_ingredient:
used to create a M:N relationship between recipes and ingredients, and to provide quantity information.
recipe_id : INT FK
relation to recipe table
ingredient_id : INT FK
relation to ingredient table
quantity : STRING
Allows recipes to list amount of each ingredient necessary (e.g. 2 cups of sugar)
ingredient_has_category:
used to create a M:N relationship between ingredients and categories
ingredient_id : INT FK
relation to ingredient table
category_id : INT FK
relation to category table
recipe_has_category:
used to create a M:N relationship between recipes and categories
recipe_id : INT FK
relation to recipe table
category_id : INT FK
relation to category table
PHP UML
For the PHP piece of the puzzle, there are five classes with five relationships. There may be a sixth class (represented by the Cookbook class in the diagram) but I think I will implement those features as functions instead of class methods in order to optimize server response time.
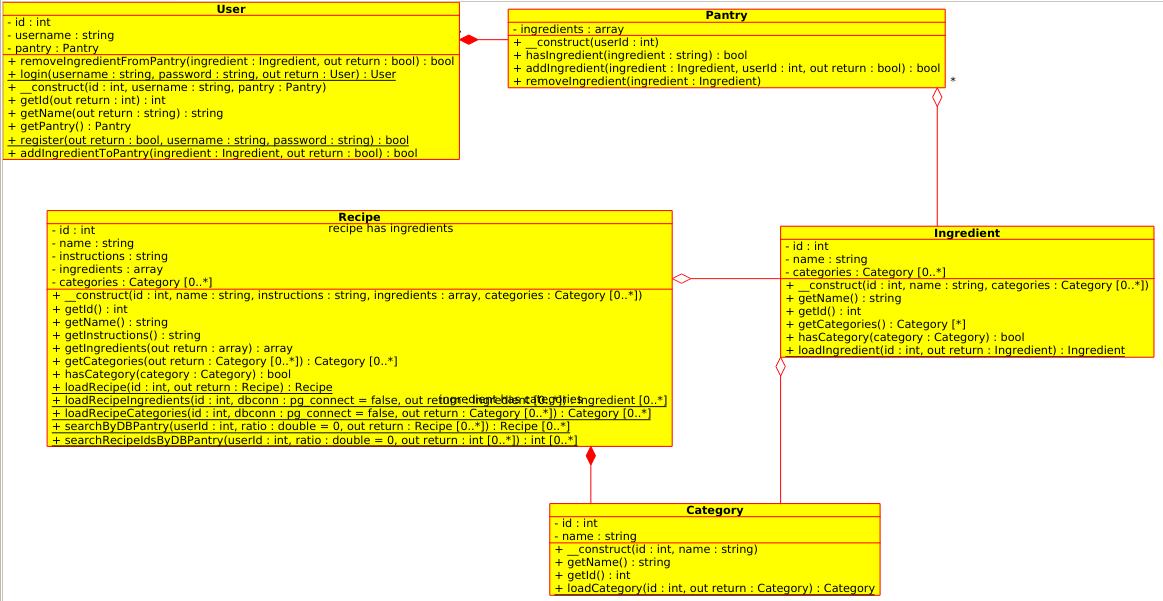
User:
This class stores user data, including a pointer to an instance of the Pantry class specific to the user. User data is pulled from the account table.
Pantry:
This class stores the list of ingredients that the User has on hand. It allows the User to add or remove ingredients. Pantry data is pulled from the user_has_ingredient table.
Ingredient:
This class stores data about each ingredient, including a list of categories. Ingredient data is pulled from the ingredient table, and the list of categories is pulled from the ingredient_has_category table.
Recipe:
This class stores data about each recipe, as well as a list of categories. Recipe data is pulled from the recipe table, and category data is pulled from the recipe_has_category table.
Category:
This class stores category data. Its data is pulled from the category table.